Konference: 2014 19th Congress of the European Hematology Association - účast ČR
Kategorie: Mnohočetný myelom
Téma: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical (Poster)
Číslo abstraktu: P369
Autoři: Prof. MD Heinz Ludwig; MD Richard Greil, Ph.D.; MD Tamas Masszi, PhD; Prof.MUDr. Ivan Špička, PhD; MD Ofer Shpilberg, MPH; prof. MUDr. Roman Hájek, CSc.; Anna Dmoszynska; Bruno Paiva; Dr. María-Belén Vidriales; Graca Esteves; MD Anne Marie Stoppa; Don Robinson jr.; Shalini Chaturvedi; MD Ozlem Ataman, PhD; Christopher Enny; Huaibao Feng; MD Helgi van de Velde, PhD
ABSSUB-4184
Background: Bortezomib in combination with thalidomide and dexamethasone (VTD) is an effective regimen in patients (pts) with previously untreated MM. We conducted an open-label phase 2 study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of VTD and VTD plus cyclophosphamide (VTDC) as induction therapy prior to high-dose therapy plus stem cell transplant (HDT/SCT) (NCT00531453). Primary results showed that both VTD and VTDC are active induction regimens resulting in bone marrow confirmed complete response (CR) rates of 29% and 31% post-induction, and 57% and 61% post-HDT/SCT, respectively (Ludwig et al. JCO 2012). There were no significant differences in efficacy between the 2 regimens, indicating no benefit from the addition of cyclophosphamide.
Aims: To assess any differences in long-term outcomes between the 2 regimens, this long-term extension follow-up phase of the study evaluated final time-to-event data: updated post-treatment results are reported.
Methods: Adult pts were randomized (1:1) to receive i.v. bortezomib (1.3 mg/m2), thalidomide (100 mg), and dexamethasone (40 mg), with or without cyclophosphamide 400 mg/m2 for 4 x 21-day cycles, followed by HDT/SCT. This long-term extension study assessed time-to-event endpoints, including time-to-next therapy (TTNT), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: 98 pts (49 VTD, 49 VTDC) were included in the intent-to-treat and safety populations. At the final analysis, median duration of follow-up was 64.8 months (65.3 months VTD, 64.7 months VTDC). Median TTNT was 51.8 months (95% CI 31.9, NE) and 47.9 months (95% CI 28.7, NE) in the VTD and VTDC treatment groups, respectively. The type of subsequent therapy was similar in both treatment groups; dexamethasone (41.8%), lenalidomide (33.7%), bortezomib (31.6%) and thalidomide (17.3%) were the most commonly used agents. In a sensitivity analysis (10 pts starting subsequent therapy after ‘relapse from CR’ or ‘clinical relapse’ but without IMWG criteria-based progression were considered to have progressed), PFS and TTP were similar in the VTD and VTDC groups: median PFS was 34.1 months (95% CI 23.5, NE) and 34.2 months (95% CI 23.5, 48.2), and median TTP was 34.7 months (95% CI 23.9, NE) and 34.5 months (95% CI 23.5, 50.6), respectively. The 3-year and 5-year OS rates were similar for both treatment groups: 79.6% (95% CI 65.4, 88.5) vs 83.7% (95% CI 70.0, 91.5) at 3 years, and 69.1% (95% CI 54.1, 80.1) vs 65.3% (95% CI 50.1, 76.8) at 5 years for the VTD and VTDC treatment groups, respectively (Figure A). Of pts with bone-marrow-confirmed CR available for MRD analysis, 34 were MRD-negative and 8 MRD-positive by multiparameter flow cytometry. When analyzed by MRD status, OS was longer in MRD-negative vs MRD-positive pts (hazard ratio [HR] 3.66, p=0.0318) (Figure B). Although not significant, a similar trend was seen for PFS (HR 2.29, p=0.0849). During this follow-up period, no new adverse events and no second primary malignancies were reported.
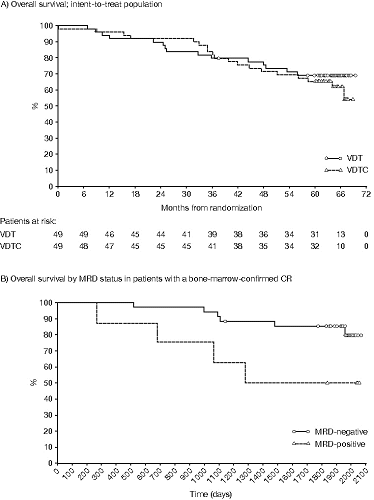
Summary/Conclusion: The VTD induction regimen followed by HDT/SCT provides long-term disease control (median TTNT 51.8 months, 5-year OS 69.1%). Consistent with the primary analysis results, there was no significant difference in long-term outcomes between the VTD and VDTC groups. Analysis of OS and PFS by MRD status confirms the importance of achieving an immunophenotypic CR after treatment.
Keywords: Bortezomib, Long-term follow-up, MRD, Myeloma
Datum přednesení příspěvku: 13. 6. 2014





