Konference: 2014 19th Congress of the European Hematology Association - účast ČR
Kategorie: Maligní lymfomy a leukémie
Téma: Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical (Poster)
Číslo abstraktu: P890
Autoři: MUDr. Lukáš Semerád; Prof. MUDr. Zdeněk Ráčil, Ph.D.; MUDr. Petra Bělohlávková; MUDr. Olga Černá; prof. MUDr. Petr Cetkovský, Ph.D.; prof. MUDr. Edgar Faber, CSc.; MUDr. Hana Klamová, CSc.; RNDr. Ludmila Malášková; Radek Minařík; Mgr. Jiřina Procházková, Ph.D.; MD Tomasz Sacha; MUDr. Jaroslava Voglová; MUDr. Daniela Žáčková, Ph.D.; Prof. MUDr. Pavel Žák, Ph.D.; prof. MUDr. Jiří Mayer, CSc.
ABSSUB-5222
Background: Recently we have published results of pilot study on CML patients demonstrating fast development of hyperinsulinaemia, peripheral insulin resistance, hypoadiponectinaemia and hypercholesterolemia during nilotinib therapy.
Aims: To analyze preliminary results from follow up study ENIGMA 2 to confirm or exclude result from the pilot study, as well as to analyze whether these abnormalities are detected in control group of patients treated with imatinib.
Methods: Patients received intensive laboratory workup before the start of TKI and after 3 month of therapy. This included fasting insulin, glucose, adiponectin and lipid serum concentration, HbA1c and oral glucose tolerance test.
Results: Between 2/2011-11/2013 twenty two CML patients initiated therapy with nilotinib and 4 with imatinib.
Patients treated with nilotinib developed significant hypersinulinaemia and hyperglycaemia. We also proved significant development of insulin resistance using HOMA-2 index, that significantly increased after 3 month of nilotinib therapy (medians - 1,8 vs. 2,5; p = 0,0098). More over, we have proved significant decrease of adiponectin concentration as well as significant increase in total cholesterol concentration. Details are presented in Table.
Contrary – none of these abnormalities was detected in the control group of patients treated with imatinib, including any change in insulin resistance measured by HOMA-2 index (medians - 0,5 vs. 0,8; p = 0,3750).
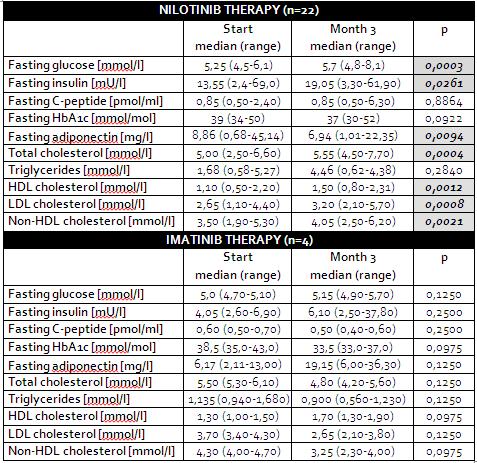
Summary/Conclusion: Our preliminary results from presented study proved fast development of peripheral insulin resistance already during the first 3 month of nilotinib therapy as underlying cause of glucose and secondary also lipid metabolism impairment during nilotinib treatment. Moreover, this was not proved for patients treated with imatinib. Final data from target of 40 patients on nilotinib and 10 patients on imatinib will be presented during the meeting.
Keywords: None
Datum přednesení příspěvku: 14. 6. 2014





