Konference: 2012 XXXVI. Brněnské onkologické dny a XXVI. Konference pro sestry a laboranty
Kategorie: Nádory hlavy a krku
Téma: 16. Nádory nervového systému
Číslo abstraktu: 152
Autoři: Ing. Josef Novotný jr., Ph.D.; P.C. Gerszten; M. Quader; V. Dewald; J.C. Flickinger
Background
Our center began a spine radiosurgery program using the Synergy S in 2007. This study prospectively evaluated a Synergy S for spine radiosurgery program, including an evaluation of patient positioning accuracy using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), treatment planning and the spinal cord and cauda equina doses received during single fraction spine radiosurgery treatments in order to determine a safety profile for this technique.
Methods
One hundred seventy-nine spine lesions were treated using the Elekta Synergy S 6-MV linear accelerator with a beam modulator and CBCT image guidance combined with a HexaPOD couch (Figure 1) that allows patient positioning correction in 3 translational and 3 rotational directions. Lesion location included 29 cervical, 76 thoracic, 52 lumbar, and 22 sacral. There were 146 malignant and 33 benign lesions. Twenty-nine lesions (16 %) were intradural. One hundred twelve lesions (63 %) had received prior conventional fractionated radiotherapy.
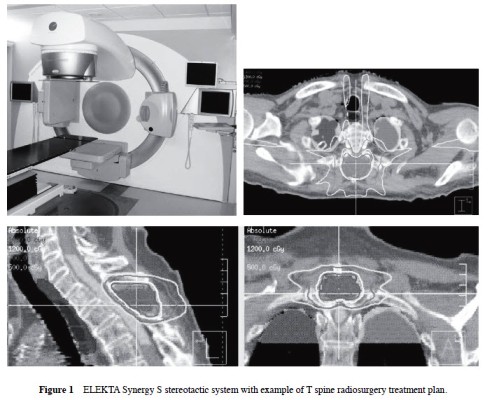
Radiosurgery was used as a primary treatment modality in 47 cases (26 %), for radiographic progression after prior conventional radiotherapy in 91 cases (51 %), and adjuvant post-surgery therapy in 41 cases (23 %). For each case, the maximum point dose to the spinal cord and/or cauda equina as well as the volume of those structures receiving greater than 8, 10, and 12 Gy were recorded. To measure intra-treatment patient movement, 3 quality assurance (QA) CBCTs were performed and recorded: immediately prior to, one-third, and two-thirds of the treatment. The positioning data and fused images of planning CT and CBCT were analyzed. From each of 3 QA CBCTs, 3 translational and 3 rotational coordinates were obtained.
Results
No subacute or delayed spinal cord or cauda equina toxicity occurred during the follow-up period (median 21 months). For cases at the level of the spinal cord (105 cases) the mean prescribed dose to the gross tumor volume (GTV) was 14 Gy (range 11-18 Gy). The GTV ranged from 0.37 to 100.24 cm3 (mean 26.1 cm3); 7 to 14 beams utilized (median 9 beams). Mean treatment time including setup was 64 minutes. The magnitude of the 3D vector was found to be 1.3±1.0 mm at one-third and 1.5±0.7 mm at two-thirds of the treatment. The mean maximum point dose to the spinal cord was 10 Gy (range 4-12 Gy), and the mean spinal cord volumes (cm3) receiving greater than 8, 10, and 12 Gy were 0.76 (0-3.45), 0.05 (0-.42), and 0.0, respectively. For cases at the level of the cauda equina the mean prescribed dose to the GTV was 15 Gy (range 10-20 Gy). The GTV ranged from 0.19 to 491.6 cm3 (mean 73.8 cm3). The mean maximum point dose to the cauda equina was 11 Gy (range 5-14 Gy), and the mean cauda equina volumes (cm3) receiving greater than 8, 10, and 12 Gy were 1.4 (0-6.68), 0.26 (0-2.99), and 0.02 (0-.3.9), respectively. No spinal cord toxicity has occurred (median follow-up 11 months).
Conclusion
Single fraction spine radiosurgery using the Synergy S was determined to be safe, feasible, and accurate. This technique provides for a translational intra fractional positioning accuracy of < 2.0 mm as observed in our study.
Datum přednesení příspěvku: 20. 4. 2012





